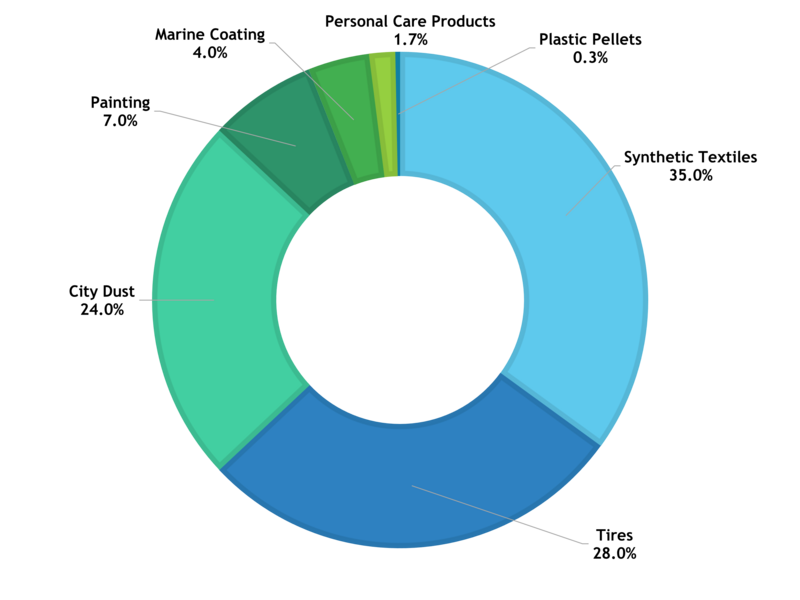
Microplastic Pollutants and the Environment
Here are eight of the key concerns associated with microplastics:
Environmental Issues
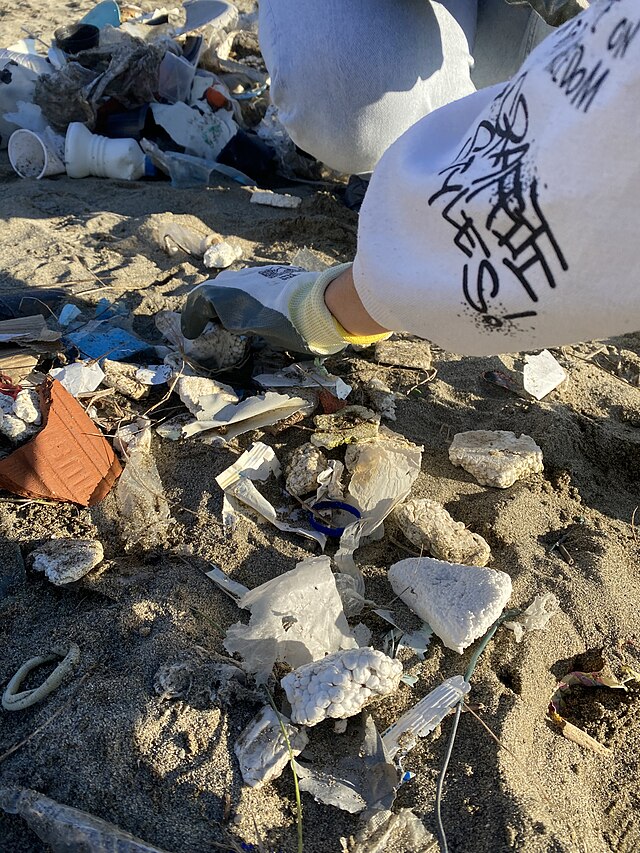
- Environmental Pollution: First, microplastics can accumulate in various environments, including oceans, rivers, lakes, and soil. They jeopardize ecosystems and biodiversity, as organisms from invertebrates to large marine mammals can ingest them. The persistence of microplastics in the environment can lead to long-term pollution.
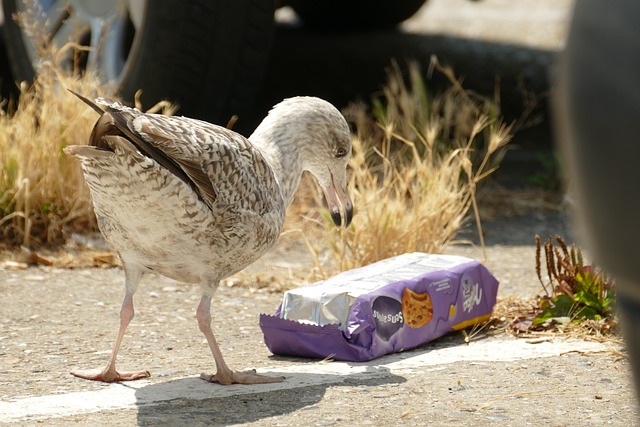
- Marine Life Impact: Secondly, aquatic organisms may mistake microplastics for food particles and ingest them. This confusion can lead to physical harm, internal damage, and blockages in the digestive systems of marine life. Sadly, the ingestion of microplastics by tiny organisms can have cascading effects throughout the food chain.
- Terrestrial Ecosystem Impact: Microplastics can also contaminate soil, affecting terrestrial ecosystems. As a result, one can detect microplastics in agricultural lands, potentially leading to the uptake of microplastics by plants. The consequences of microplastic pollution in terrestrial environments are still an area of ongoing research.
- Airborne Transport: Microplastics can become airborne, leading to their presence in the atmosphere. This phenomenon can result from the breakdown of plastic items and the release of microplastics from products like synthetic clothing during washing. Therefore, the deposition of airborne microplastics may have implications for air quality.