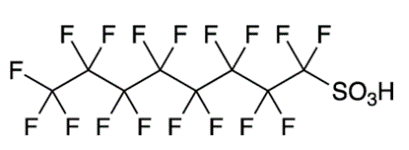
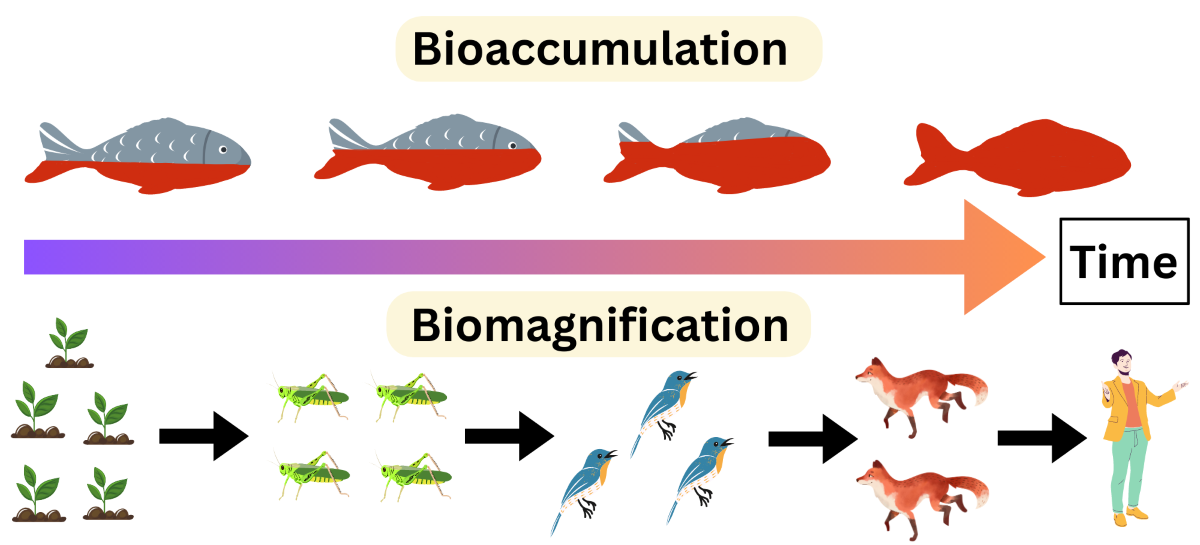
Due to several factors related to its chemical structure and interactions with biological organisms, PFOS is considered toxic. For example:
- Studies have linked perfluorooctane sulfonates exposure to various health issues, including liver damage, kidney dysfunction, immune system suppression, thyroid disruption, developmental delays, and reproductive problems.
- Experts have associated prenatal exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonates with reduced birth weight, altered immune function, and potential developmental effects in infants and child.
- Accumulation of PFOS in breast milk has raised concerns about its transfer to infants during breastfeeding.
- Also, PFOS can bind to proteins disrupting natural physiological processes in the body. For example, it can affect serum albumin in blood plasma, hormone receptors, enzymes, and protein-mediated cellular transport.