When managing the sale of electronic devices, it is crucial to adhere to the laws restricting the substances used. Specifically, RoHS regulations aim to protect human health and the environment restricting certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment. This directive originating in the European Union (EU) has become global practice, with many countries having similar regulations.
Notably, the following countries also have RoHS regulations:
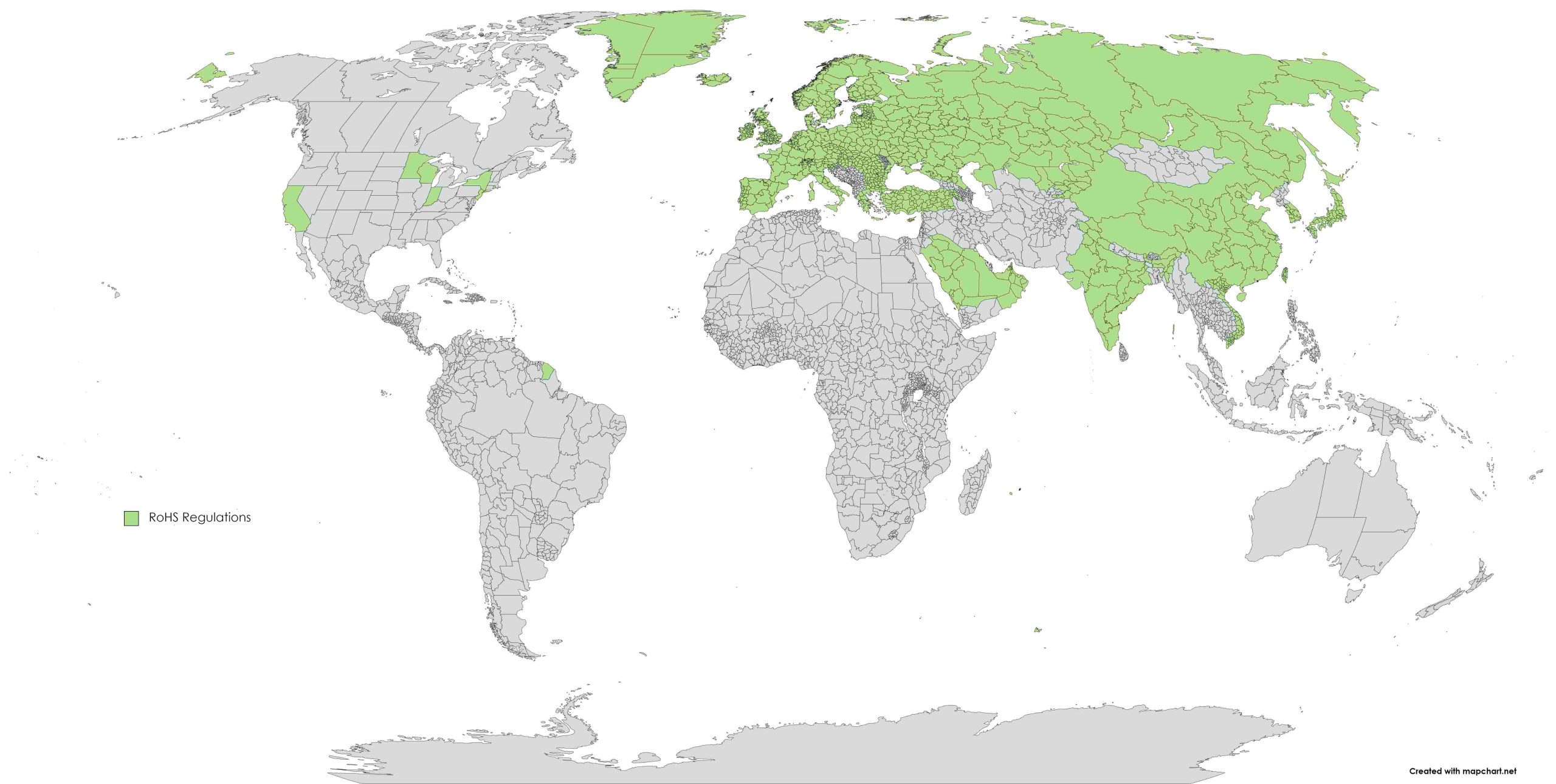
Although each country regulations have the same intent of preventing the use of toxic substances from the design, there are differences in the application.
The differences between the regulations exist in the hereafter mentioned elements:
EU | Turkey | Ukraine | UK | India | China | Saudi Arabia | UAE | EAEU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Phthalates* | ✓ | X | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | X | ✓ | X |
Label | X |
| X | or | |||||
Applicable Technical Standards | IEC 62321 IEC 62476 | = | = | = | = | GBT 26572-2011 SJ/Z 11388-2009 SJ/T 11364-2014 | IEC 63000 SASO IEC 62321 SASO IEC TR 62476 | ISO 17025 IEC 62321 | Same as the EU, referenced as regulation: TR CU 037/2016 |
Notified Body | X | X | X | X | X | X | SASO | ESMA | X |
*Inclusion of the EU Directive 2015/863 to include four phthalates
Note: = indicates countries where the criteria are similar or the same to the EU
The in-scope product categories are the same in most countries as with EU RoHS, with a few exceptions:
EU | Turkey | Saudi Arabia | India | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Scope | 1. Large household appliances. 2. Small household appliances. 3. IT and telecommunications equipment. 4. Consumer equipment. 5. Lighting equipment. 6. Electrical and electronic tools. 7. Toys, leisure, and sports equipment. 8. Medical devices. 9. Monitoring and control instruments, including industrial monitoring and control instruments. 10. Automatic dispensers. Other EEE not covered by any of the categories above. | Scope includes the ten first EU RoHS product categories | 1. Home appliances 2. Information and communication technology equipment 3. Lighting equipment 4. Electrical and electronic tools and equipment 5. Play, leisure, and sports equipment 6. Monitoring and control devices |
|
An important aspect while comparing RoHS practices is the substances regulated, the limits set for each substance, and the exemptions that apply.
Every country has the same concentration limits posed under the initial EU directive 2011/65/EU restricting six substances:
Substance | Concentration Limit |
|---|---|
Lead (Pb) and lead compounds | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
Cadmium (Cd) and cadmium compounds | 0.01% or 100 ppm |
Mercury (Hg) and mercury compounds | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
Hexavalent chromium (Cr 6+) and hexavalent chromium compounds | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
Polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
*ppm= parts per million
The aspects in this category where we see differences are the inclusion of the EU Directive 2015/863 to include four phthalates:
Substance | Concentration Limit |
|---|---|
Butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP) | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
Di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP) | 0.1% or 1000 ppm |
Not every country has regulated these phthalates in electronics. For example, Turkey includes them from January 1st, 2024.
Additionally, the RoHS exemptions lists of each country have some variance from those of the EU. The difference in phthalates and exemptions are summarized below:
Country | Inclusion of Phthalates | Exemptions |
|---|---|---|
EU | ✓ | General and Medical Devices and Monitoring and Control Instruments exemptions |
India | X | Yes |
Turkey | ✓ from Jan 1st, 2024 | Yes |
Ukraine | ✓ | Yes |
China | ✓ | No. Declarable substances that exceed the limits |
UK | ✓ | Yes |
Saudi Arabia | X | Different exemption references |
UAE | ✓ | Yes |
EAEU | X | Yes |
In addition, there is a difference in the labels used to identify products as RoHS compliant in each country.
Country | Label |
|---|---|
EU | European Conformity (CE): |
India | None |
Turkey | Same as the EU. CE mark accepted. |
Ukraine | Decree no 1184 or UkrSEPRO: |
China | Environmentally Friendly Use Period (EFUP): No substances above the limits: If any substance is above its limit: Demonstrating the number of years in which no hazardous substances would leak or mutate under normal conditions |
UK | United Kingdom Conformity Assessed: |
Saudi Arabia | None |
UAE | 2 acceptable markings: Emirates Quality Mark (EQM) obtained by Product Certification Scheme Method: Certificate of Conformity (ECAS) obtained by Registration Scheme Method: |
EAEU | Eurasian Conformity Mark (EAC): |
RoHS standards are the recommendations a manufacturer follows to demonstrate RoHS conformity. The main international standards are:
These countries have adopted to following standards:
Country | Applicable Technical Standards |
|---|---|
China |
|
Saudi Arabia | Product Certificate of Conformity (PCoC): ISO/IEC 17067 Type 1a assessment
|
Turkey | Same as the EU, referenced as regulation: TR CU 037/2016 |
UAE | 2 Methods for obtaining RoHS conformity certificates: Registration Scheme Method:
Product Certification Scheme Method:
|
Finally, a notified body is an organization officially designated by a country to assess the conformity of a product, in this case, regarding RoHS. As previously demonstrated in the summary table, these countries require RoHS-notified bodies:
On top of RoHS regulations worldwide, other environmental requirements apply to electronics.
Contact Enviropass for any questions on RoHS regulations!